Tsundere Bot Replaces Initial Access Hackers in Ransomware Attacks
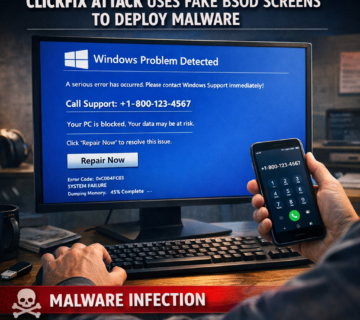
Cybercriminal group TA584 has dramatically evolved its tactics, replacing traditional initial access hackers with advanced malware like Tsundere Bot. This sophisticated malware platform, part of a broader trend in the malware-as-a-service economy, allows attackers to bypass traditional defenses and execute fileless attacks. Tsundere Bot is enabling more efficient ransomware deployments, posing an increasing threat to businesses across multiple industries. Learn how this new wave of malware affects organizations and how to protect against such evolving threats in this comprehensive guide. ... Read More