Understanding The Findlay Group Cyber Breach and Class Action Lawsuit
Get Your Free Copy Now! Click the link below and fill out the form to access the white paper.
In an era of escalating cyber threats, the Findlay Group cyber breach stands out as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities companies face. This article provides an in-depth look at the breach, the subsequent class action lawsuit, and offers a whitepaper on how to protect your organization from similar threats.
Overview of the Findlay Group Cyber Breach
Initial Discovery: In early June 2024, the Findlay Group’s IT department detected unusual activity on their network. An initial investigation revealed unauthorized access, prompting immediate action.
Timeline of Events
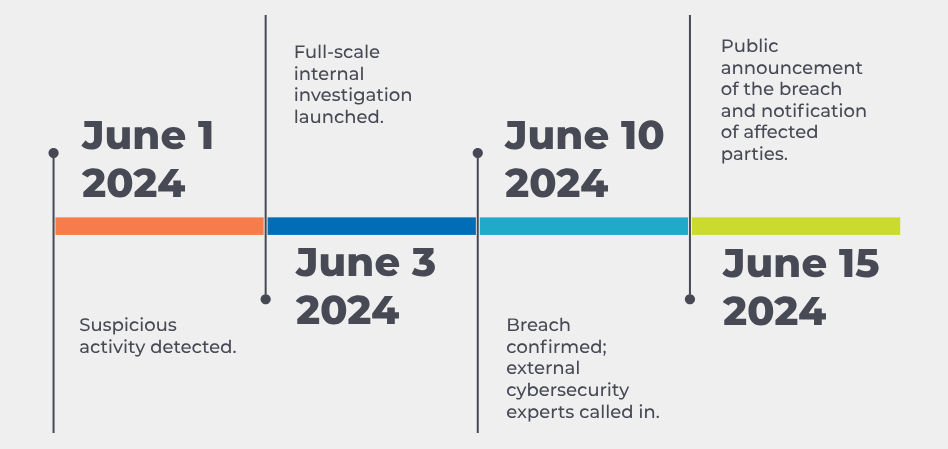
Scope of the Breach: The breach affected sensitive data, including personal and financial information of clients and employees. The attackers had been active within the system for several weeks prior to detection.
How the Breach Occurred
- Vulnerabilities Exploited: Hackers exploited outdated software vulnerabilities in the Findlay Group’s network. These weaknesses allowed them to bypass security measures and gain access.
- Methods Used by Hackers: Phishing emails were the initial entry point. Once inside, malware was deployed to escalate privileges and move laterally within the network.
- Security Lapses: The breach was exacerbated by delayed software updates and insufficient monitoring, which provided opportunities for the attackers to exploit the system.
Impact on the Findlay Group

- Financial Losses: The financial impact was substantial, including fines, legal fees, and compensation for affected clients. Restoring and securing the systems added further costs.
- Reputational Damage: The breach significantly damaged the Findlay Group’s reputation, leading to loss of client trust and business opportunities.
- Operational Disruptions : Operational disruptions included service delays and compromised business continuity, with the recovery process being both time-consuming and costly.
Details of the Class Action Lawsuit
- Grounds for the Lawsuit: Affected clients and employees filed a class action lawsuit against the Findlay Group, citing negligence in protecting sensitive data and failing to prevent the breach.
- Parties Involved : The lawsuit included multiple plaintiffs representing individuals whose data was compromised. Legal firms specializing in cybersecurity and data protection represented the plaintiffs.
- Legal Outcomes :The lawsuit led to a settlement agreement, with the Findlay Group agreeing to pay significant compensation to the affected parties and committing to enhanced cybersecurity measures.
Data Compromised in the Breach

- Types of Data Affected: The breach compromised personal identification information (PII), financial records, and confidential business information.
- Personal Information: Sensitive personal data, including Social Security numbers, addresses, and contact details, were exposed, posing risks of identity theft and fraud.
- Corporate Data :Confidential corporate information, such as strategic plans and proprietary data, was also accessed, leading to potential competitive disadvantages.
Immediate Response by Findlay Group
- Incident Response Team: An incident response team, comprising internal IT staff and external cybersecurity experts, was assembled to address the breach.
- Containment Measures: Immediate actions included isolating affected systems, updating security protocols, and enhancing network monitoring to prevent further unauthorized access.
- Communication with Stakeholders : The Findlay Group promptly informed clients, employees, and regulatory authorities about the breach, providing transparency and updates on the ongoing investigation and mitigation efforts.
Investigation into the Breach
- Forensic Analysis : A thorough forensic analysis was conducted to understand the full extent of the breach, identify entry points, and gather evidence for the investigation.
- Involvement of Law Enforcement : Law enforcement agencies were involved to trace the cybercriminals behind the breach and pursue legal action. Collaboration with authorities helped uncover the attackers’ methods.
- Key Findings : The investigation revealed critical security weaknesses and provided insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by the attackers. These findings informed future security strategies.
Lessons Learned from the Breach
- Identified Weaknesses: The breach highlighted specific weaknesses in the company’s cybersecurity framework, such as outdated software and inadequate monitoring.
- Steps Taken to Improve Security: The Findlay Group implemented measures to strengthen their security posture, including regular software updates, enhanced threat detection, and comprehensive employee training programs.
- Industry Implications: The breach serves as a cautionary tale for other companies, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures and proactive risk management strategies.
Preventive Measures for Companies

- Enhancing Cybersecurity: Invest in advanced security technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection, to protect against cyber threats.
- Employee Training: Regular cybersecurity training for employees is crucial for creating awareness about common threats like phishing and social engineering. Educated employees form a strong line of defense.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct frequent security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are up to date. Utilize both internal teams and external experts for comprehensive assessments.
Importance of Cyber Insurance
- Coverage Options: Cyber insurance provides financial protection in the event of a breach. Policies typically cover costs related to data recovery, legal fees, and public relations efforts.
- Benefits: Cyber insurance mitigates the financial impact of a breach, enabling companies to recover more quickly and efficiently.
- Selecting the Right Policy : Choose a policy that fits your company’s specific needs, considering factors such as the nature of the data handled and the overall risk profile.
Role of Government and Regulations
- Compliance Requirements : Companies must comply with various cybersecurity regulations and standards, such as ISO/IEC 27001, to ensure the protection of sensitive data.
- Data Protection Laws: Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) mandate strict data protection practices and impose heavy fines for non-compliance.
- Impact of GDPR and CCPA: These regulations have set high standards for data privacy and protection, compelling companies to enhance their cybersecurity measures to avoid penalties and safeguard customer trust.
Best Practices for Data Protection
- Strong Passwords: Encourage the use of strong, unique passwords and implement password management tools to reduce the risk of password-related breaches.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide additional verification beyond just a password.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data, both at rest and in transit, to ensure that even if intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains unreadable and secure.
The Human Element in Cybersecurity
- Social Engineering Attacks: Educate employees about social engineering attacks, such as phishing and pretexting, to help prevent these tactics from being successful.
- Employee Awareness: Ongoing awareness programs keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices, making them active participants in the company’s cybersecurity efforts.
- Insider Threats: Implement strict access controls and monitoring systems to detect and mitigate insider threats, whether malicious or accidental.
Future of Cybersecurity
- Emerging Threats: Stay informed about emerging threats like ransomware-as-a-service and deepfake attacks to remain prepared for future cyber challenges.
- Advances in Technology: Advancements in cybersecurity technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are enhancing threat detection and response capabilities.
- Role of AI in Security: AI-driven security tools analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that indicate potential threats, thereby improving overall security posture.
FAQs
What was the Findlay Group cyber breach?
The Findlay Group cyber breach was a significant cybersecurity incident where hackers gained unauthorized access to sensitive data, including personal and financial information of clients and employees.
How did the breach occur?
The breach occurred due to vulnerabilities in the Findlay Group’s network, which were exploited by hackers using phishing emails and malware.
What data was compromised in the breach?
The breach compromised personal identification information (PII), financial records, and confidential business information.
What was the outcome of the class action lawsuit?
The class action lawsuit resulted in a settlement agreement, with the Findlay Group agreeing to pay significant compensation to affected parties and committing to enhanced cybersecurity measures.
What steps did Findlay Group take in response to the breach?
The Findlay Group assembled an incident response team, contained the breach, communicated with stakeholders, and implemented enhanced security measures to prevent future incidents.
How can companies prevent similar breaches?
Companies can prevent similar breaches by enhancing cybersecurity measures, conducting regular security audits, providing employee training, and investing in cyber insurance.



