Tsundere Bot Replaces Initial Access Hackers in Ransomware Attacks
🎙️ Dive Deeper with Our Podcast!
As threat actors modify their strategies to get beyond contemporary security solutions, the cybersecurity landscape keeps changing. Recent observations by security researchers have uncovered a concerning shift in the operations of a prolific cybercriminal group, signaling potential dangers for organizations worldwide.
The Rising Threat of TA584
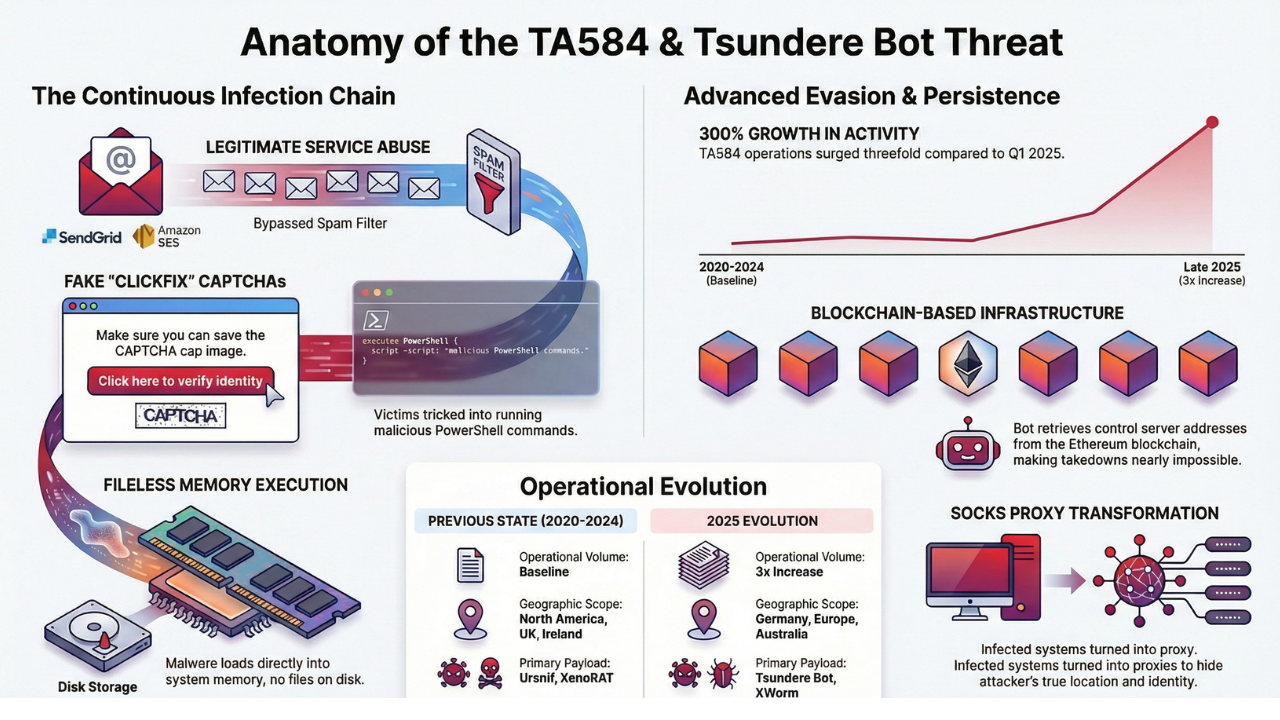
A sophisticated cybercriminal operation known as TA584 has dramatically escalated its attack campaigns, introducing advanced malware tools that pose significant risks to businesses and institutions globally. This threat actor, which security researchers have monitored since 2020, has recently tripled its operational volume and expanded its targeting scope beyond traditional boundaries.
The group now employs Tsundere Bot, a relatively new malware platform, alongside XWorm remote access trojan to compromise networks. These tools serve as gateways for more devastating attacks, including ransomware deployments that can cripple entire organizations.
Understanding Tsundere Bot
Tsundere Bot represents a new generation of malware-as-a-service platforms that combines backdoor functionality with sophisticated loader capabilities. Initially documented by cybersecurity firm Kaspersky, this malicious software originates from Russian-speaking operators with connections to other known malware families.
The platform operates with remarkable technical sophistication. It requires Node.js to function properly, which the malware automatically installs on victim systems using custom installers generated from its command-and-control infrastructure. This approach allows the malware to blend in with legitimate software installations, making detection more challenging for traditional security tools.
Technical Capabilities
Tsundere Bot demonstrates several advanced features that make it particularly dangerous:
The malware retrieves its command-and-control server addresses from the Ethereum blockchain using a variant of the EtherHiding technique. This innovative approach makes takedown efforts significantly more difficult, as the infrastructure isn’t dependent on traditional domain names or IP addresses that authorities can easily block. The malware also includes hardcoded fallback addresses to maintain persistence even if blockchain retrieval fails.
Communication between infected systems and control servers occurs over WebSockets, providing real-time bidirectional communication channels. This architecture enables threat actors to respond quickly to changing circumstances and execute commands with minimal delay.
The platform includes system profiling capabilities that collect detailed information about infected machines, helping attackers identify high-value targets and plan subsequent attack stages. It can execute arbitrary JavaScript code received from command servers, providing virtually unlimited flexibility for malicious operations.
Perhaps most concerning is its ability to transform infected hosts into SOCKS proxies. This functionality allows cybercriminals to route traffic through compromised systems, obscuring their actual locations and making attribution more difficult for law enforcement and security researchers.
The Evolution of Attack Chains
TA584 has refined its infection methodology to create what researchers describe as a continuous attack chain that effectively undermines static detection mechanisms employed by many security solutions.
Initial Compromise
The attack sequence begins with carefully crafted email campaigns. These messages originate from hundreds of compromised email accounts that have been dormant or aging for some time, lending them an air of legitimacy that helps bypass spam filters and security gateways.
The threat actors leverage legitimate email delivery services including SendGrid and Amazon Simple Email Service. By abusing these trusted platforms, the attackers benefit from the established reputation of these services, significantly increasing the likelihood that malicious emails will reach their intended targets.
Each email contains unique URLs tailored to individual recipients. This personalization serves multiple purposes: it complicates blocklist-based defenses, enables tracking of which targets interact with the malicious content, and allows attackers to apply granular filtering based on recipient characteristics.
Sophisticated Filtering
The campaign employs multiple layers of filtering to ensure only intended targets proceed through the infection chain. Geofencing restricts access based on geographic location, while IP filtering examines the requesting address against predefined criteria.
Victims who pass these initial checks encounter redirect chains that often incorporate third-party traffic direction systems such as Keitaro. These intermediary systems add additional layers of obfuscation, making it more difficult for security researchers to trace the full attack infrastructure.
Social Engineering Components
After navigating the redirect chain, targets arrive at a page displaying a CAPTCHA challenge. This familiar element exploits user expectations about web security, as many legitimate websites employ CAPTCHAs to verify human users. By mimicking this common security measure, attackers create a false sense of legitimacy.
Following the CAPTCHA, victims encounter a ClickFix page that presents instructions for running a PowerShell command on their system. These instructions often claim to resolve a technical issue or verify the user’s identity, leveraging social engineering to convince targets to execute malicious code willingly.
Execution Phase
When users run the provided PowerShell command, it triggers a sophisticated infection sequence. The command retrieves an obfuscated script from attacker-controlled infrastructure, then loads either XWorm or Tsundere Bot directly into system memory without writing files to disk.
This fileless approach presents significant challenges for traditional antivirus solutions that rely on scanning files stored on disk. By operating entirely in memory, the malware reduces its forensic footprint and increases the difficulty of detection and analysis.
After establishing the infection, the PowerShell script redirects the victim’s browser to a benign website. This final deception helps mask the compromise, as users see what appears to be a legitimate website and may not realize anything suspicious occurred.
Expanded Targeting and Scale
The scale and scope of TA584 operations have grown substantially. Activity during late 2025 showed a threefold increase compared to the first quarter of that year, demonstrating the group’s expanding capabilities and ambitions.
Geographic targeting has broadened considerably beyond the traditional focus on North America, the United Kingdom, and Ireland. Recent campaigns have included Germany, various other European nations, and Australia, suggesting the threat actors are seeking opportunities across multiple regions and markets.
This geographic expansion likely reflects several factors: saturation of traditional target regions, opportunities in markets with different security postures, and efforts to diversify operations to reduce risk concentration.
Historical Payload Arsenal
Throughout years of operation, TA584 has demonstrated flexibility in payload selection, utilizing various malware families depending on specific objectives and circumstances.
The group has previously deployed Ursnif, a banking trojan with data theft capabilities that has been active for over a decade. LDR4 and WarmCookie have served as intermediate loaders and information stealers in various campaigns. XenoRAT provided remote access capabilities before the adoption of Tsundere Bot and XWorm.
Cobalt Strike, a legitimate penetration testing framework frequently abused by threat actors, has appeared in TA584 operations for post-exploitation activities. DCRAT, another remote access trojan, was still observed in at least one campaign during 2025, indicating the group maintains multiple tools in its arsenal.
This diverse toolkit allows TA584 to adapt to different target environments, bypass specific security solutions, and maintain operations even if defenders develop countermeasures against particular malware families.
The Ransomware Connection
Security researchers assess with high confidence that Tsundere Bot infections could lead to ransomware deployments. The malware’s capabilities align perfectly with the requirements of ransomware operators who need to gather intelligence, move laterally through networks, and exfiltrate data before deploying file-encrypting payloads.
Initial access brokers like TA584 often sell network access to ransomware operators or collaborate directly with ransomware groups. The compromised systems and credentials obtained through these infection campaigns provide ransomware actors with the foothold they need to launch devastating attacks.
Data exfiltration capabilities enable double extortion ransomware tactics, where attackers not only encrypt files but also threaten to publish stolen sensitive information if ransom demands aren’t met. Lateral movement features allow attackers to spread through networks, maximizing impact and increasing leverage during ransom negotiations.
Defense Evasion Techniques
Tsundere Bot incorporates several mechanisms designed specifically to avoid detection and analysis by security researchers.
The malware checks system locale settings during execution and aborts if it detects Commonwealth of Independent States country languages, particularly Russian. This behavior serves multiple purposes: it reduces the likelihood of infecting systems in countries where the operators reside, potentially avoiding local law enforcement attention, and provides a geographical indicator that can help with attribution efforts.
The use of blockchain-based command-and-control address retrieval represents a sophisticated approach to maintaining operational infrastructure. Traditional takedown efforts target domain names and IP addresses, but blockchain-stored information cannot be easily removed or modified without controlling the relevant private keys.
Memory-only execution leaves minimal traces on infected systems, complicating forensic analysis and making it more difficult for security teams to understand the scope and nature of a breach. Obfuscated PowerShell scripts challenge automated analysis tools that might otherwise quickly identify malicious behavior.
The Malware-as-a-Service Economy
Tsundere Bot operates as a malware-as-a-service platform, complete with a built-in marketplace where infected systems can be bought and sold. This business model has become increasingly common in the cybercrime ecosystem, lowering barriers to entry and enabling less technically sophisticated criminals to launch effective attacks.
The marketplace feature allows initial access brokers to monetize compromised systems efficiently, selling access to the highest bidders. Different buyers might have varying interests: ransomware operators seeking lucrative targets, data thieves looking for specific information, or advanced persistent threat groups requiring footholds in particular networks.
This commoditization of cybercrime creates a more fluid and dynamic threat landscape. Organizations might face attacks from multiple distinct groups that all originated from a single initial compromise, complicating incident response and attribution efforts.
Future Threat Evolution
Security researchers anticipate that TA584 will continue evolving its tactics and expanding its operations. The group’s history demonstrates a willingness to experiment with different payloads, adapt to defensive measures, and pursue new opportunities.
Expected developments include broader targeting across additional geographic regions and industry sectors. The threat actors will likely continue testing new malware families and infection techniques to identify the most effective approaches against current defensive technologies.
As security solutions improve their detection capabilities, TA584 will presumably develop more sophisticated evasion techniques. The continuous adaptation characteristic of advanced threat actors ensures that the cybersecurity community must remain vigilant and proactive rather than reactive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an initial access broker?
An initial access broker is a cybercriminal who specializes in compromising computer systems and networks, then selling that access to other malicious actors. These brokers serve as the first stage in many sophisticated cyberattacks, providing ransomware operators and other threat groups with entry points into target organizations.
How does Tsundere Bot differ from traditional malware?
Tsundere Bot distinguishes itself through several advanced features including blockchain-based command-and-control infrastructure, memory-only execution to avoid disk-based detection, and a built-in marketplace for selling compromised systems. These characteristics make it more resilient against takedown efforts and harder for security tools to detect.
Can antivirus software detect these attacks?
Traditional signature-based antivirus solutions struggle with these attacks due to the fileless execution methods and continuous evolution of the malware code. More advanced endpoint detection and response solutions that monitor behavior rather than just file signatures offer better protection, though no security tool provides absolute certainty.
What industries are most at risk from TA584?
While TA584 has demonstrated broad targeting across multiple sectors, organizations with valuable data or critical operations face elevated risk. Healthcare, financial services, manufacturing, and government entities frequently attract attention from initial access brokers due to their willingness to pay ransoms or the value of their information.
How can organizations tell if they’ve been compromised?
Indicators of compromise include unusual PowerShell activity, unexpected network connections particularly to blockchain-related services, the presence of Node.js installations without clear business justification, and anomalous user account behavior. However, sophisticated attackers often operate below the threshold of normal detection, making professional security assessments valuable.
What should I do if I receive a suspicious email with unusual links?
Never click links or run commands from unexpected emails, even if they appear to come from known contacts. Verify requests through alternative communication channels, report suspicious messages to your IT security team, and when in doubt, delete the message without interacting with any elements.
Are small businesses targets for these attacks?
Absolutely. While large enterprises attract significant attention, small and medium-sized businesses often have fewer security resources and may be seen as easier targets. Initial access brokers don’t discriminate by size, and compromised small business systems can serve as stepping stones to larger partners or suppliers.
How long can attackers remain undetected in a network?
Dwell time varies significantly, but sophisticated threat actors can maintain presence in compromised networks for months or even years before being detected. During this period, they gather intelligence, escalate privileges, and position themselves for maximum impact when they eventually execute their primary objective.
How Technijian Can Help
At Technijian, we understand that the evolving cybersecurity threat landscape demands comprehensive, proactive protection strategies. Our team of experienced security professionals specializes in defending organizations against sophisticated threats like those posed by TA584 and emerging malware platforms.
We offer advanced email security solutions that go beyond traditional spam filtering to identify and block sophisticated phishing campaigns, malicious URLs, and social engineering attempts before they reach your users. Our multi-layered approach examines sender reputation, content analysis, and behavioral patterns to catch threats that simpler systems miss.
Our endpoint detection and response capabilities provide real-time monitoring and threat hunting across your entire infrastructure. Unlike traditional antivirus that relies on known signatures, our solutions identify suspicious behaviors like unusual PowerShell activity, fileless malware execution, and anomalous network connections that indicate compromise.
Technijian’s security awareness training programs educate your team to recognize and respond appropriately to social engineering tactics. We transform your employees from potential vulnerabilities into an active defense layer through engaging, practical training that addresses real-world attack scenarios.
Our incident response team stands ready to assist if you suspect a compromise. We provide rapid assessment, containment, eradication, and recovery services to minimize damage and restore normal operations. Our forensic capabilities help identify the scope of breaches, while our remediation expertise ensures threats are completely removed.
We also offer comprehensive security assessments that identify vulnerabilities in your current defenses before attackers exploit them. Our penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security architecture reviews provide actionable insights for strengthening your security posture.
For organizations requiring ongoing support, our managed security services provide continuous monitoring, threat intelligence integration, and expert analysis. We become an extension of your team, delivering enterprise-grade security capabilities regardless of your organization’s size or internal resources.
Contact Technijian today to discuss how we can help protect your organization against ransomware attacks, initial access brokers, and the full spectrum of cybersecurity threats. Our commitment is to provide practical, effective security solutions tailored to your specific needs and risk profile.
About Technijian
Technijian is a premier managed IT services provider in Irvine, specializing in delivering secure, scalable, and innovative AI, SEO, and technology solutions across Orange County and Southern California. Founded in 2000 by Ravi Jain, what started as a one-man IT shop has evolved into a trusted technology partner with teams of engineers, AI specialists, cybersecurity professionals, and digital marketing experts both in the U.S. and internationally.
Headquartered in Irvine, we provide comprehensive cybersecurity solutions, IT support, AI implementation services, cloud services, and search engine optimization (SEO) and digital visibility solutions throughout Orange County—from Aliso Viejo, Anaheim, Costa Mesa, and Fountain Valley to Newport Beach, Santa Ana, Tustin, and beyond. Our extensive experience with enterprise telecommunications and security deployments, combined with our expertise in SEO-driven growth strategies and our deep understanding of local business needs, makes us the ideal partner for organizations seeking solutions that deliver real protection, online visibility, and operational efficiency.
We work closely with clients across diverse industries, including healthcare, finance, law, retail, and professional services, to design integrated technology and SEO strategies that reduce risk, enhance productivity, improve search rankings, and strengthen digital presence while maintaining the highest protection standards. Our Irvine-based office remains our primary hub, delivering the personalized service and responsive support that businesses across Orange County have relied on for over two decades.
With expertise spanning cybersecurity, managed IT services, telecommunications, AI implementation, SEO and digital marketing, consulting, and cloud solutions, Technijian has become the go-to partner for small to medium businesses seeking reliable technology infrastructure and measurable online growth. Whether you need 3CX deployment in Irvine, telecommunications optimization in Santa Ana, IT consulting in Anaheim, or SEO services to increase visibility and lead generation, we deliver solutions that align with your business goals and operational requirements.
Partner with Technijian and experience the difference of a local IT company that combines global technology expertise, SEO-driven growth, and community-focused service. Our mission is to help businesses across Irvine, Orange County, and Southern California harness the power of advanced technology and digital marketing to stay protected, visible, efficient, and competitive in today’s digital world.